Table of Contents
What is Bariatric Surgery?
Bariatric surgery is a procedure that helps individuals lose weight by altering the digestion system in some way. This surgery can be classified into restrictive vs malabsorptive bariatric surgery, where some surgeries reduce the size of the stomach (restrictive), while others affect how nutrients and calories are absorbed (malabsorptive).
The stomach is either made smaller, decreasing how much you can eat, or the intestines are rerouted, impacting how fat and calories are digested and absorbed. This procedure is intended to help individuals with morbid obesity who have been unsuccessful with all other weight loss methods and are facing obesity-related health complications.
Compared to other weight loss methods, many wonder about the comparison of bariatric surgery vs liposuction, with bariatric surgery offering more long-term solutions by addressing both consumption and absorption.
Successful bariatric surgery can positively impact the individual’s life by resulting in significant weight loss, improving obesity-related health conditions, providing more energy, alleviating pain, and enhancing quality of life.
When considering bariatric surgery cost, it is crucial to evaluate not only the financial aspects but also the long-term health benefits that come from sustained weight loss and improved overall health.
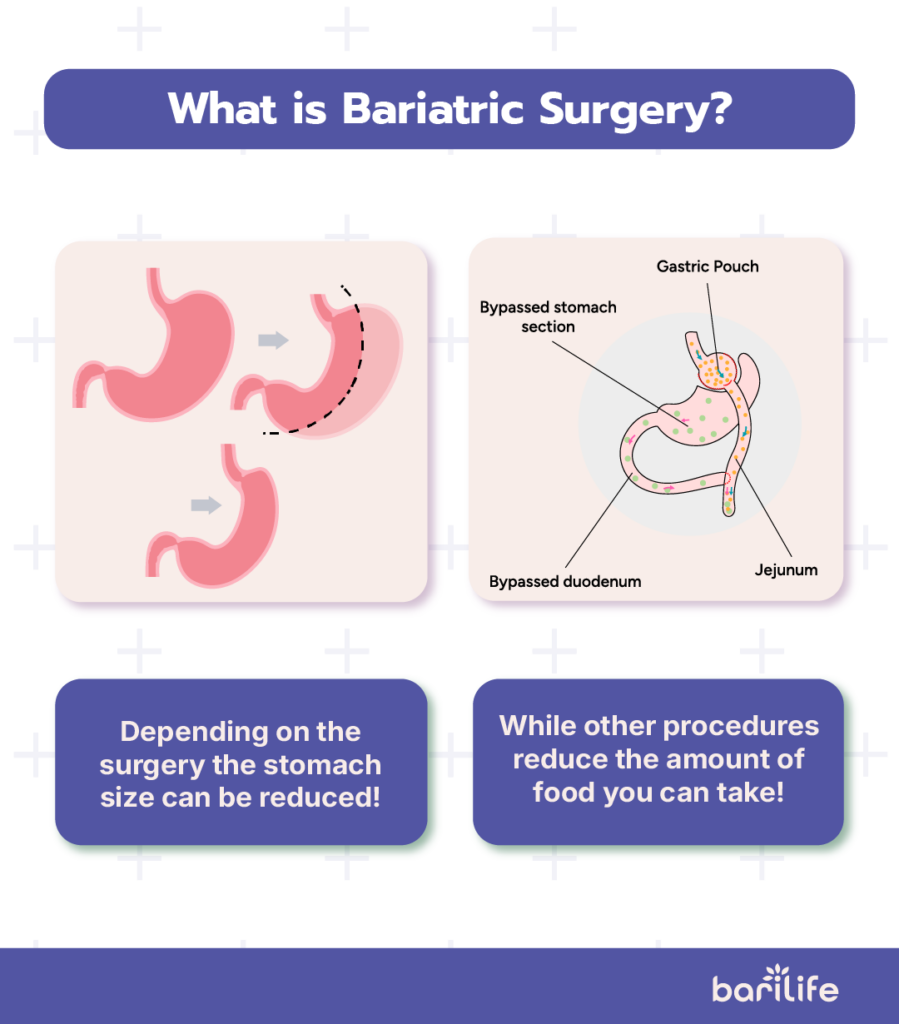
Types of Bariatric Surgery Procedures
There are several types of bariatric surgery. Each has unique pros and cons.
Gastric bypass, also called Roux-en-Y, works by restricting food intake and reducing absorption. A small stomach pouch is created and the small intestine is rerouted to attach directly to the pouch. The food is bypassing most of the stomach and the beginning of the small intestine, decreasing the absorption rate.
Gastric sleeve works by reducing the stomach size and limiting food intake. The stomach is turned into a tube-like structure, which reduces its size by about 80%. This surgery reduces the amount of hunger hormones that your stomach can produce.
Adjustable gastric band involves placing a band around the upper part of the stomach, which creates a small pouch and works by restricting food intake. This procedure presents with lower weight loss results, as it is a restrictive type only and does not affect absorption.
When comparing robotic vs laparoscopic bariatric surgery, it is important to consider factors such as precision, recovery time, and potential complications. Robotic surgeries may offer enhanced dexterity and visualization, while laparoscopic techniques are less invasive than traditional open surgeries, both being effective options for bariatric patients.
Benefits of Bariatric Surgery
Successful bariatric surgery has many benefits. Weight loss is the primary outcome. If the patient adheres to lifestyle changes following the surgery it can help them achieve sustained weight loss, which can alleviate or resolve obesity-related health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, and hypertension.
Overall, bariatric surgery can improve quality of life by enhancing mobility, self-esteem, and reducing the risk of future health complications.
To maintain the results, patients often rely on bariatric multivitamins, including bariatric vitamins for overall health and bariatric vitamins for hair loss. These are especially important post-surgery as nutrient absorption is reduced.
Who is a Candidate for Bariatric Surgery?
Candidates for bariatric surgery include individuals who have a BMI of 40 or higher, or have a BMI of 35+ with obesity-related health conditions such as type 2 diabetes. Additionally, a candidate for bariatric surgery must have previously attempted other weight loss methods without success. A psychological evaluation is commonly needed to assess a patient’s mental health, ensuring they are prepared for the lifestyle changes after surgery. Since higher BMIs are associated with a greater prevalence of eating disorders, anxiety, and mood disorders, it is crucial to evaluate a person’s mental well-being before undergoing a life-altering procedure.

Preparation for Bariatric Surgery
Before bariatric surgery, one must prepare. This includes counseling, tests, and lifestyle changes.
Patients are often placed on a high-protein diet before surgery, which may include bariatric protein shakes or bariatric snacks. These dietary preparations help patients adjust to the changes they will need to maintain post-surgery. In addition, liquid bariatric vitamin supplements may be recommended for easier absorption in the early stages of recovery.
These preparations ensure the best possible outcomes and minimize risks. In some cases, patients are placed in a ramped position bariatric to ensure proper airway management and reduce potential complications during surgery.
Before surgery, patients must meet specific nutritional requirements to prepare for post-operative changes. They may need to lose weight first. This requires a diet change a few months ahead. Patients must follow a high-protein, low-carb, low-fat, full-liquid diet for one to two weeks before the procedure.
A medical evaluation, which includes blood tests, imaging, and a review of medical history, is conducted to assess the risks related to the procedure. This evaluation helps identify, evaluate, and address comorbidities that may increase the risk of complications during surgery. A thorough preoperative assessment is essential for improving outcomes in bariatric surgery patients.
You must make lifestyle changes before surgery. This will reduce risks and improve recovery. Diet and exercise help prepare the body for surgery.
What are the Lifestyle Changes I Will Need to Make After Bariatric Surgery?
After surgery, lifestyle changes will need to be made in order to maintain weight loss.
Dietary changes include following a specific diet, which will start with fully liquid items directly after surgery with a slow transition to solid foods. Long-term dietary intake should focus on high protein and low sugar foods. Specific goals include consuming 60-100 grams of lean protein per day, consuming small frequent meals, consuming 6-8 cups of water per day, and supplementing with necessary vitamins and minerals. Lifelong supplementation of vitamins and minerals may be required following certain bariatric surgeries due to changes in nutrient absorption.
Regular physical activity following bariatric surgery is essential to maintain weight loss and improve overall health. You should start with light activity such as walking as soon as it is approved by your doctor, and then you should aim to exercise 30 minutes per day. Physical activity helps improve recovery time and increase the procedures outcomes.

Common Misconceptions about Bariatric Surgery
There are many misconceptions regarding bariatric surgery. Many believe that the procedure is an easy way out, or a quick fix. The truth is that bariatric surgery is not a one-step process to lose weight. The procedure requires significant effort, both prior to surgery and following surgery. The patient must make life-long lifestyle changes for success.
Moreover, the misconception that all procedures are irreversible is incorrect, as some surgeries, such as the adjustable gastric band, are examples of reversible bariatric surgery and another misconception is that bariatric revision surgery is uncommon. However, for patients who experience complications or inadequate weight loss after their initial surgery, revision surgery can offer a second chance at achieving successful outcomes.
A common belief is that the patient will inevitably regain the weight after surgery. With proper adherence to lifestyle changes following surgery, long-term results are possible. It is important that the patient receives proper postoperative screenings and follow ups to assess adherence and recovery.
Another common misconception about bariatric surgery is that it is highly risky and unsafe. While every surgery carries some risk, bariatric procedures have become significantly safer over the years due to technological advancements and improved preoperative care. Moreover, for individuals with severe health conditions caused by morbid obesity, such as cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes, the benefits of bariatric surgery often outweigh the risks.
Conclusion
Bariatric surgery can be an effective tool for managing severe obesity, but long-term success depends on a lifelong commitment to new habits. It provides a valuable option for those facing obesity-related health problems. However, before deciding on bariatric surgery, individuals should carefully consider the pros and cons and create a plan that aligns with their lifestyle goals. This significant decision should be made in consultation with a medical team to ensure it’s the right choice.



What are your tips and tricks to post-bariatric success?