One common concern about what is bariatric surgery? is that it’s often considered irreversible. While most bariatric procedures cannot be undone, some surgeries do offer the possibility of reversal.
Table of Contents
Types of Reversible Bariatric Surgery
Adjustable gastric banding is a reversible bariatric procedure which involves placing a band around the stomach to create a small pouch, limiting food intake. This band has a hollow channel which allows for adjustability and personalized treatment via saline injections. The band can be removed, returning the stomach to its original form. This procedure also illustrates the concept of restrictive vs malabsorptive bariatric surgery as it focuses on restricting food intake without affecting nutrient absorption.
Patients undergoing this surgery often need to supplement their diet with bariatric vitamins, including bariatric multivitamins and/or bariatric multivitamin with iron, to ensure proper nutrient absorption post-surgery.
An intragastric balloon is a non-surgical and reversible procedure that can temporarily have an impact on weight loss. It is typically in place for six months to one year and can be removed without any permanent changes. The balloon works by reducing appetite – it is inserted into the stomach and inflated to occupy space.
Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) is a non-surgical procedure that uses sutures to reshape the stomach into a smaller sleeve. It can be reversed by releasing the sutures. If this is reversed in a short time frame, the stomach can return to normal. This reversal has a higher rate of complications due to the nature of the procedure, yet it results in less complications than traditional gastric sleeve surgeries.
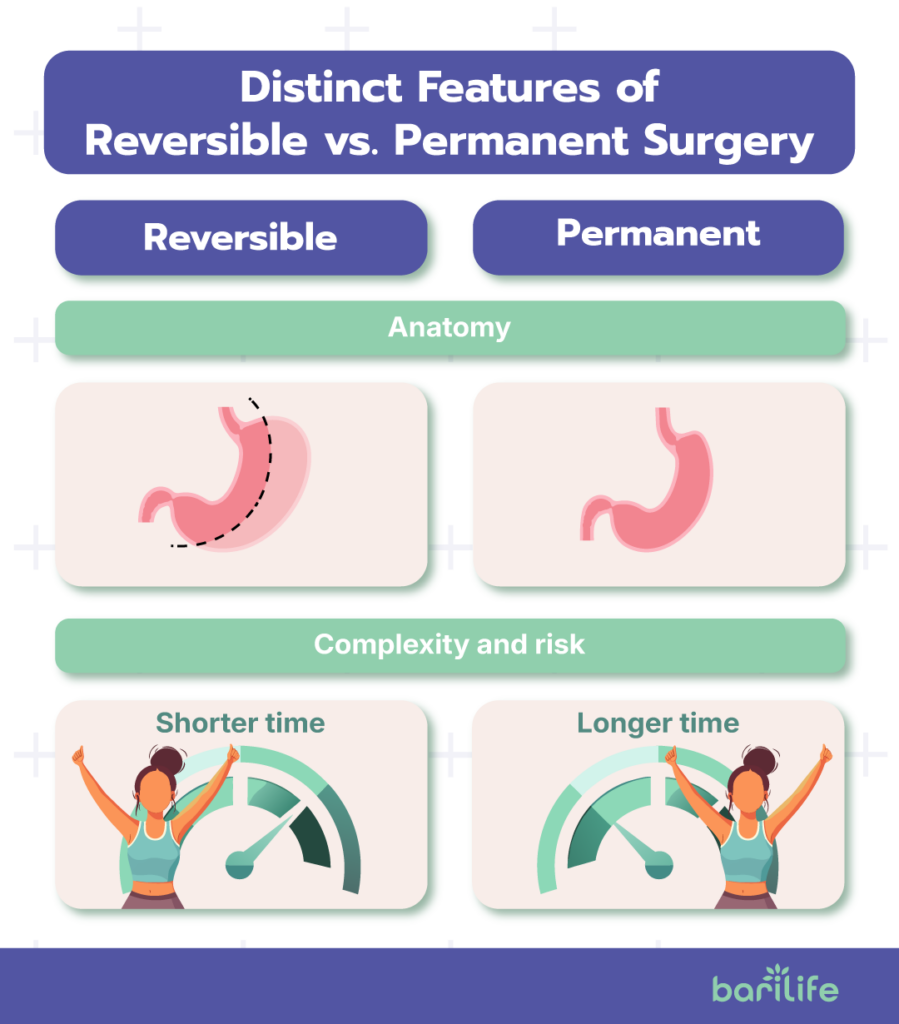
Distinct Features of Reversible vs. Permanent Surgery
| Reversible | Permanent | |
| Anatomy | Does not alter anatomy permanently, patients can return to normal physiology. | Involves removing or bypassing parts of the stomach or intestines, creating lifelong anatomy changes. |
| Complexity and risk | Less invasive, lower immediate risks and complications. | Greater risks and longer recovery times. |
| Long-term effectiveness | Slower and less dramatic weight loss, may need additional procedures and lifestyle adjustments to maintain weight loss | May provide more substantial weight loss when lifestyle changes are maintained following surgeries. Potential need for life-long nutritional supplementation. |
When considering these options, it’s crucial to understand the bariatric surgery cost associated with each type. Permanent surgeries might have higher initial costs due to their complexity, but reversible procedures may require future interventions, adding to the overall cost.
Factors Influencing Reversibility
Factors that influence whether there is an option for reversibility includes the type of procedure, the surgeon’s expertise, and the patient’s health.
Types of procedures that are designed to be fully reversed include adjustable gastric banding and intragastric balloon. Other types of procedures that are designed to permanently alter the stomach cannot be fully reversed, but may be able to be partially reversed in order to accommodate the patient’s needs. A Gastric sleeve cannot be reversed due to part of the stomach being removed. A Gastric bypass is partially reversible, however it involves going through a surgery that is of the same magnitude as the original procedure and poses many risks.
Choosing a skilled surgeon who specializes in performing and reversing bariatric procedures is crucial. Not all surgeons who specialize in bariatric surgery also specialized in the reversal of bariatric surgery. A more complex procedure may result in complications that make reversal riskier, requiring a surgeon that has a vast understanding of these risks.
The patient’s health is another critical factor. Pre-existing health conditions may prevent you from being eligible for a reversal, and your overall health can impact the safety and risks involved. Similar to the initial bariatric surgery, a bariatric revision surgery will likely require both a nutritional and psychological assessment beforehand.
Safety Considerations for Reversing Procedures
Although reversible procedures tend to have lower complication rates initially, they do carry their own risks including infection, bleeding, scarring, hernias, or damage to surrounding organs, and nutrient deficiencies. Patients may need to take bariatric vitamins chewable or liquid bariatric vitamin post-reversal to ensure proper nutrient absorption. Long-term safety post-reversal depends on careful monitoring and adherence to health guidelines.
Additionally, is bariatric surgery safe is an important question to consider, especially when assessing the safety of the procedure and potential reversals.
Long-term nutritional status may be affected after a bariatric surgery reversal, particularly if you previously underwent a permanent procedure like gastric bypass, which alters nutrient absorption. During the recovery phase, it is essential to seek nutritional counseling to adjust your supplementation and diet based on individual needs.
Mental health should be addressed by professionals such as therapists and psychologists. Reversing a bariatric surgery can have a significant psychological impact, especially if you experience weight regain. There should be a focus on addressing body image issues and maintaining a positive outlook.
Candidacy for Reversible Bariatric Surgery
Patients who have a BMI of 30-40, have not been able to lose weight through all other methods, and who are looking for a less invasive weight-loss surgery may be ideal candidates for reversible bariatric surgery such as intragastric balloon, adjustable gastric banding, and ESG.
Additionally, patients who have received a permanent bariatric procedure such as a gastric sleeve or a gastric bypass and are facing complications associated with the surgery, may consider revisional bariatric surgery. Candidacy for reversible surgeries is evaluated based on overall health and goals specific to the individual.
Oftentimes, patients prefer reversible options due to the fear of permanent changes. Reversible surgeries offer peace-of-mind for individuals who are interested in the surgery, yet concerned about the long-term effects or complications.
Reversible bariatric surgeries are not recommended for patients with a BMI over 40 or those who need rapid and significant weight loss due to certain conditions. Additionally, individuals with medical issues such as gastrointestinal disorders, severe psychiatric conditions, end-stage organ disease, or a history of substance abuse may not benefit from these procedures. A thorough medical evaluation is required to identify any contraindications that could increase the risk of complications.
Expected Weight Loss Outcomes
It is expected that reversible procedures will often result in slower, more gradual weight loss compared to permanent options. Final weight loss with reversible surgeries such as gastric banding has an average weight loss of one third to one half of the extra weight the patient was carrying. Long-term success and weight-loss maintenance is heavily dependent on patient adherence to lifestyle changes including dietary intake and physical activity. The risk of weight regain is higher in reversible surgeries when compared to permanent surgeries, and the effectiveness of the procedure may decrease over time.

With reversible procedures there is the potential need for reoperation. Refilling the gastric band or replacing an intragastric balloon may be required. If patients do not achieve their desired weight loss, they may opt for a permanent procedure. Oftentimes, patients who are severely obese will choose to get an intragastric balloon procedure prior to a permanent surgery to decrease preoperative risks.
Reversible bariatric surgery offers an option for patients who may later choose to undo the procedure. It is important to remember that not all surgeries are suitable for reversal and choosing to reverse them can pose medical risks. When choosing a bariatric surgery that is right for you, there should be special consideration of health status, including potential contraindications and the need for thorough preoperative assessments.
Conclusion
Most bariatric surgeries are irreversible. But, some can reverse. They offer options to patients worried about permanent changes. Reversible bariatric surgeries reduce appetite or limit food intake. They are: adjustable gastric banding, intragastric balloon, and ESG.
These surgeries do not permanently change the stomach’s anatomy. These procedures are less invasive. They have lower immediate risks. But, they often lead to slower weight loss. They need to make strict lifestyle changes for lasting success.
Reversibility depends on the procedure, the surgeon, and the patient’s health. Reversing these surgeries has risks. These include nutrient deficiencies and mental health issues. Ideal candidates for reversible bariatric surgery are those with a BMI of 30 to 40. They have not lost weight with other methods. They prefer less invasive options. But, they may not suit those needing quick, major weight loss or with some medical issues. Ultimately, choose the right bariatric surgery. Weigh the health, risks, and pre-op tests.




What are your tips and tricks to post-bariatric success?