When it comes to bariatric surgery, you may face the crucial decision between restrictive and malabsorptive procedures. Each type offers unique benefits and potential drawbacks, making it essential to understand how they differ. The bariatric surgery cost and bariatric surgery safe aspects should also be carefully considered during the decision-making process.
Restrictive surgeries, such as gastric sleeve and band, limit stomach capacity. This promotes a feeling of fullness sooner. In contrast, malabsorptive procedures, like biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch, reduce stomach size and bypass most of the small intestine, potentially necessitating the use of bariatric multivitamins to compensate for reduced nutrient absorption.
This article explores the pros and cons of each approach, helping prospective patients navigate their options and make informed decisions about their weight loss journey, including considerations for bariatric revision surgery or the choice between Restrictive vs Malabsorptive Bariatric Surgery
Table of Contents
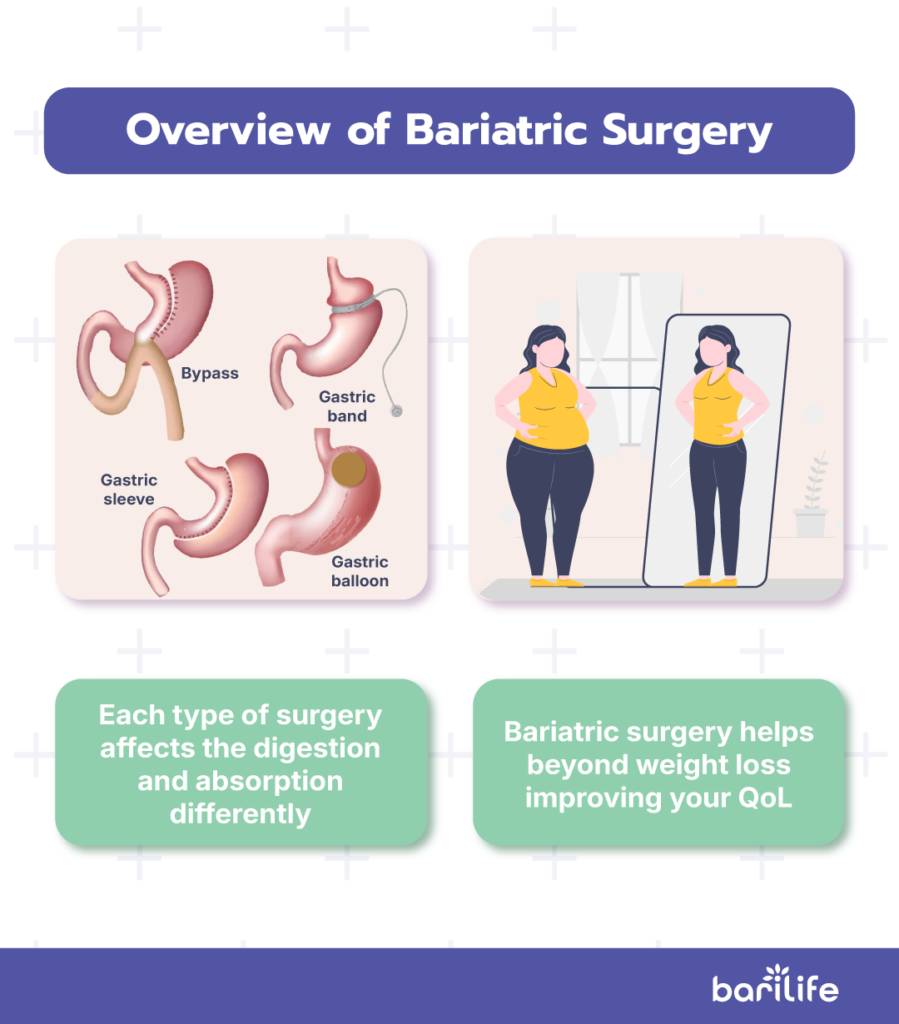
Overview of Bariatric Surgery
What is bariatric surgery? Bariatric surgery offers several approaches to aid in weight loss, including gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD/DS).
Each of these methods affects digestion and calorie absorption differently, leading to varying weight loss outcomes. Most surgeries are performed laparoscopically, meaning they involve smaller incisions and typically allow for quicker recovery compared to traditional open surgery.
Beyond weight loss, bariatric surgery can have significant health benefits, such as reducing the risk of obesity-related conditions like type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and sleep apnea.
It is also worth considering whether a procedure qualifies as a reversible bariatric surgery to ensure the best long-term fit for your health goals. You can experience improvements in your quality of life, including increased physical mobility and reduced joint pain.
Additionally, you can experience improvements in your quality of life, including increased physical mobility and reduced joint pain. Long-term results can be impressive, with studies showing that patients may lose 50% or more of their excess weight within two years, depending on the procedure and their commitment to lifestyle changes.
What are Malabsorptive Bariatric Procedures?
Malabsorptive bariatric procedures, such as BPD/DS and its modification, Single Anastomosis Duodenoileostomy with Sleeve Gastrectomy (SADI-S), work by rerouting food so that it bypasses much of the small intestine.
This leads to a significant reduction in nutrient absorption, which often requires patients to take bariatric vitamins regularly to prevent deficiencies.
Because less of the small intestine is used, these surgeries are particularly effective at treating metabolic conditions like type 2 diabetes, as they impact gut hormones and hunger signals in a way that promotes better blood sugar control.
However, the reduced nutrient absorption also comes with a higher risk of nutritional deficiencies. Patients who undergo these procedures are more likely to experience long-term deficiencies in vitamins and minerals, making regular medical follow-ups and ongoing supplementation essential to avoid complications.
Although these surgeries can offer impressive results, careful management of nutrition is key to maintaining overall health.
What are Restrictive Bariatric Procedures?
Restrictive bariatric procedures, such as gastric sleeve and adjustable gastric band (AGB), focus on reducing the size of the stomach. By making the stomach smaller, these surgeries limit the amount of food that can be eaten at one time, which helps reduce overall calorie intake.
Unlike malabsorptive procedures, restrictive surgeries don’t change the way food is digested or absorbed by the body. Instead, they work by promoting a feeling of fullness more quickly, which encourages smaller portion sizes.
One of the main advantages of these procedures is that they are less complex and carry a lower risk of nutritional deficiencies, since they don’t directly interfere with nutrient absorption. However, they may not always be as effective for long-term weight management compared to malabsorptive surgeries, particularly for patients with metabolic conditions like type 2 diabetes.
Comparing Weight Loss Outcomes
When comparing weight loss outcomes from different bariatric procedures, gastric bypass tends to be one of the most effective options, with patients typically losing around 70% of their excess body weight. Sleeve gastrectomy is also effective, often resulting in weight loss in the range of 60-70%. The biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD/DS) has the potential for the highest weight loss among these options; however, it comes with a greater risk of complications.
Beyond just the amount of weight lost, many bariatric surgeries significantly improve or even lead to the complete remission of comorbid conditions like type 2 diabetes and hypertension within just a few months after surgery, regardless of how much weight has been lost.
Long-term success in weight loss is measured not only by how much weight a person loses but also by their ability to keep it off. Research shows that over 90% of patients can maintain at least 50% of their excess weight loss in the long run, especially when they engage in proper follow-up care and commit to making lifestyle changes. This emphasizes the importance of ongoing support and healthy habits after surgery, ensuring that the benefits of the procedure extend well beyond the initial weight loss phase.

Recovery and Lifestyle Changes
Recovering from bariatric surgery involves a careful and gradual process to help your body adjust to its new way of functioning. Initially, you will start with a liquid diet, moving on to soft foods before finally transitioning to regular meals. This reintroduction of food takes several weeks and is crucial for proper healing.
Certain positions, like the ramped position bariatric, can aid in the recovery process by improving breathing and reducing postoperative discomfort.
In addition to dietary adjustments, making long-term lifestyle modifications is essential. You will need to commit to eating smaller meals and avoiding high-calorie foods that can sabotage their progress. Regular physical activity is also a key component in sustaining weight loss.
Follow-up care is vital in the recovery journey. Regular visits to healthcare providers and periodic blood tests are necessary to monitor nutritional status and ensure adherence to dietary guidelines and supplement intake. This ongoing support will help you stay on track and make any needed adjustments to their health plans.

Patient Suitability and Individual Considerations
When it comes to determining patient suitability for bariatric surgery, several important factors come into play. Candidates are typically individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher, or those with a BMI of 35 or higher who also suffer from obesity-related health conditions such as type 2 diabetes or hypertension.
Before undergoing surgery, patients often need to prepare by following a specific pre-surgical diet aimed at reducing intra-abdominal fat. This not only helps to make the procedure safer but also sets the stage for post-surgery weight loss success. Additionally, patients are usually required to participate in counseling and mental health evaluations.
Certain conditions, such as drug or alcohol abuse, severe psychiatric disorders, or reversible causes of obesity, may disqualify a patient from undergoing the procedure. This comprehensive approach ensures that patients who proceed with surgery are well-equipped to handle the changes that come with it, ultimately leading to more successful outcomes in their weight loss journey.
Conclusion
Choosing between restrictive and malabsorptive bariatric surgery is a significant decision that requires careful consideration. Each approach comes with its own set of benefits and challenges, and understanding these can help you make an informed choice that aligns with your health goals and lifestyle.
Restrictive procedures like gastric sleeve and adjustable gastric banding focus on limiting food intake, while malabsorptive procedures, such as biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch, go further by affecting nutrient absorption. Both types of surgery have proven effective in achieving substantial weight loss and improving obesity-related health conditions.
However, ongoing support, lifestyle changes, and regular follow-up care are essential for sustaining long-term success. By weighing the pros and cons and considering your unique circumstances, you can find the right path toward a healthier future.



What are your tips and tricks to post-bariatric success?