Are you having trouble deciding which bariatric surgery is right for you? As you will discover, each bariatric procedure has its own pros, cons, and expected weight loss. In this article, we review weight calculations, expected weight loss, and the pros and cons of the different bariatric surgeries. To make it easier, we also have a bariatric weight loss chart, that shows how much weight you should lose over time.
Reviewing the Basics
Before reviewing our bariatric weight loss chart, we need to review the basics. Some basic calculations include body mass index (BMI), ideal weight, and excess weight loss.
Body Mass Index
Your body mass index (BMI) is a calculation based on your height and weight. It determines your body size and your amount of body fat. A BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 is healthy. If your BMI is between 25 and 29.9, you are overweight.
Anything greater than 30, and you are considered obese. To qualify for bariatric weight loss surgery, usually, your BMI has to be greater than 35 and you have comorbidities, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, etc. Other bariatric surgeries require candidates to have a BMI greater than 40.
Ideal Weight
Now that we’ve discussed BMI, another important aspect to know is your ideal weight. The chart below shows ideal body weights based on your gender and body frame size. Bariatric surgery patients should use this chart as a resource for their long-term weight loss goals.
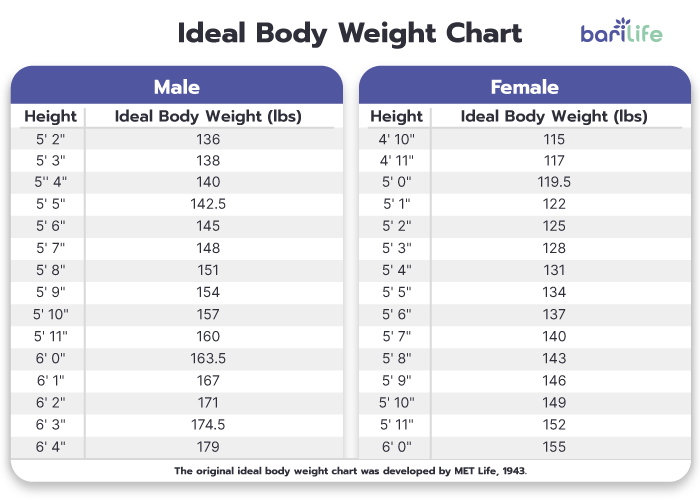
Calculating Excess Weight
Excess weight is the amount of weight over your ideal body weight. For example, you are a 5’9” male with a large frame, who currently weighs 250lbs. If you refer to the ideal body weight chart above, your ideal weight is at least 176lbs, which is at the top of the range. So you would take:
Current weight – ideal weight= amount of excess weight
250lbs – 176lbs= 74lbs excess weight
Therefore, you need to lose 74lbs to be in your ideal body weight range.
Percentage of Excess Weight Loss
Excess weight loss is the amount of weight you could lose after bariatric surgery to meet your ideal weight. Usually, this is referred to as percentage excess weight loss (%EWL). Different bariatric surgeries have an average %EWL, based on the procedure.
For example, you currently weigh 250lbs and the %EWL with your surgery is 60%. According to the chart above, your ideal weight is 176lbs. We determined that your excess weight was 74lbs. Next, to calculate your estimated weight loss from bariatric surgery, you would do as follows:
Amount of excess weight x average percentage of %EWL for the procedure= Estimated weight loss from bariatric surgery
74lbs x 60%= 44.4lbs estimated weight loss
Percent Excess Weight Loss by Procedure Type
As mentioned above, there are different percentages of %EWL, depending on the procedure. Let’s review the %EWL by procedure type.
Gastric Bypass (Roux-en-Y): 65-80%
Sleeve Gastrectomy (Gastric Sleeve): 50-70%
Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD with DS): 70-80%
Gastric Band: 50%
Intragastric Balloon: 10% in 6 months
If you want to calculate your excess weight loss by procedure, here is a great calculator.
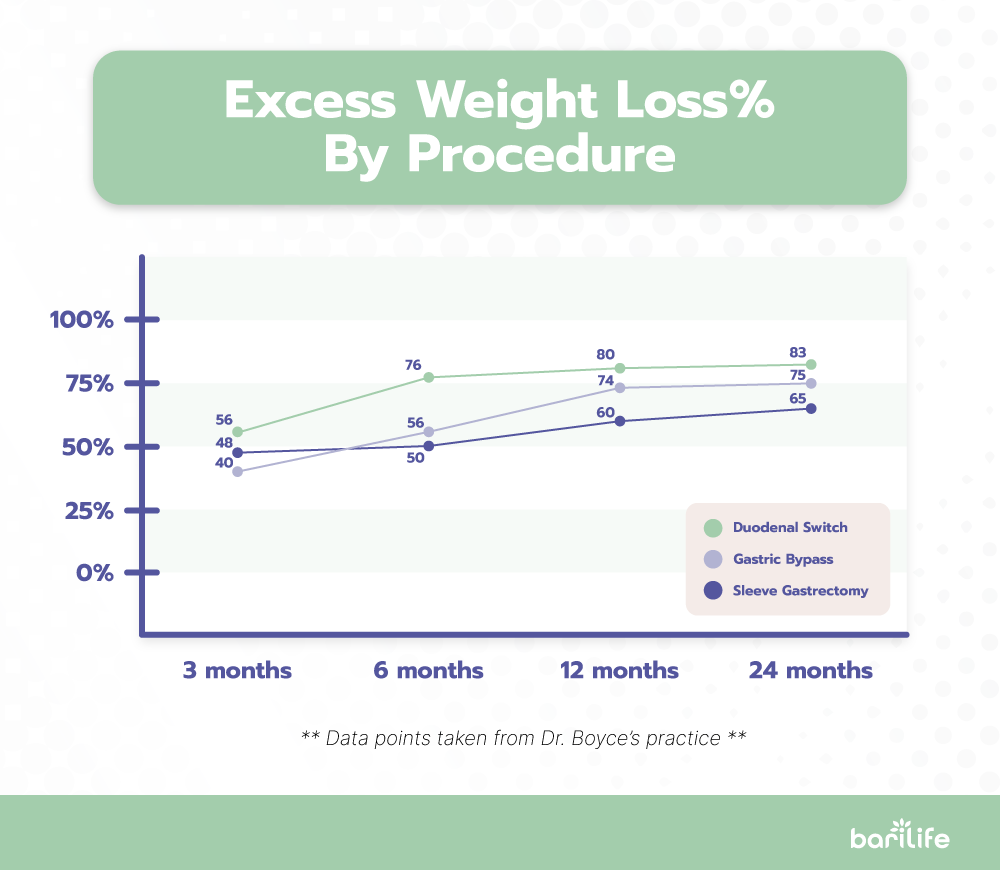
Bariatric Weight Loss Chart
Next, let’s discuss the average weight loss over time by procedure type and the pros and cons of each procedure.
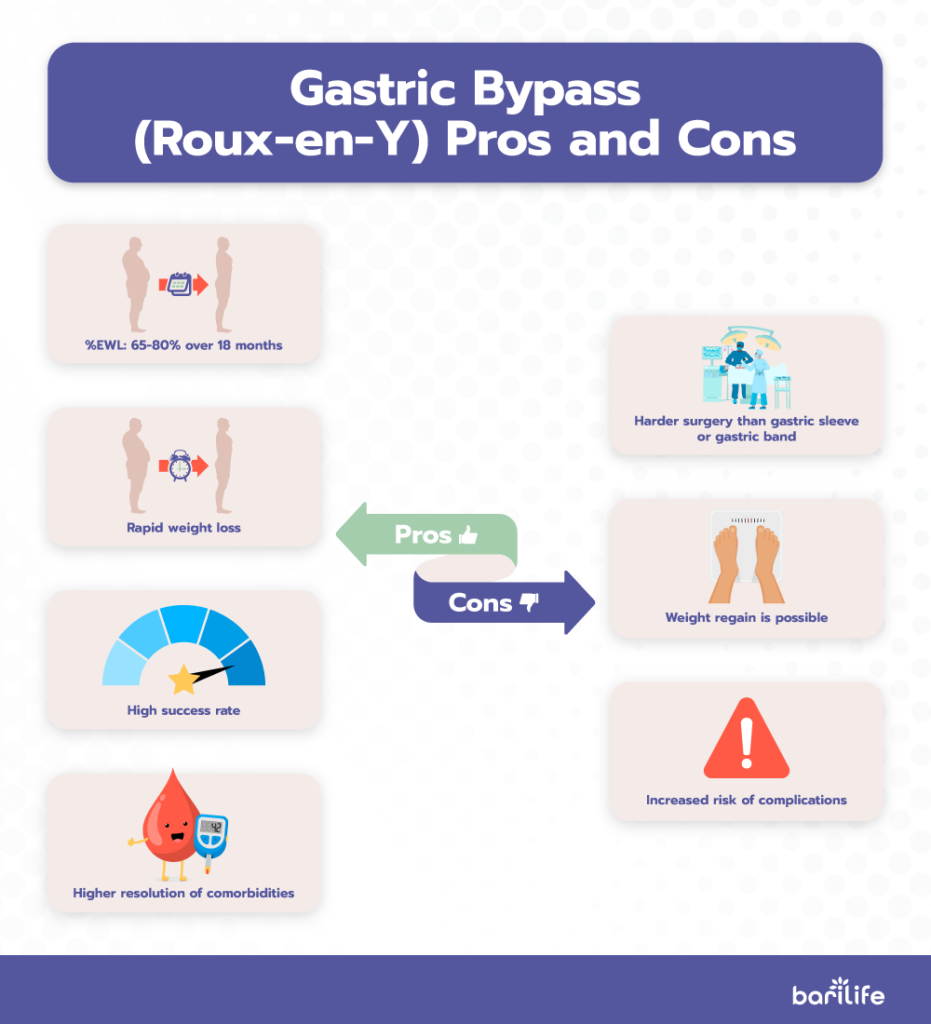
1. Gastric Bypass (Roux-en-Y)
As you can see from the bariatric weight loss chart, gastric bypass surgery has one of the highest percentages of excess weight loss when compared to other procedures.
Pros
- %EWL: 65-80% over 18 months
- Rapid weight loss
- High success rate
- A higher resolution of comorbidities, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, etc.
Cons
- Harder surgery than gastric sleeve or gastric band
- Weight regain is possible
- Increased risk of complications, such as small bowel obstructions or hernias
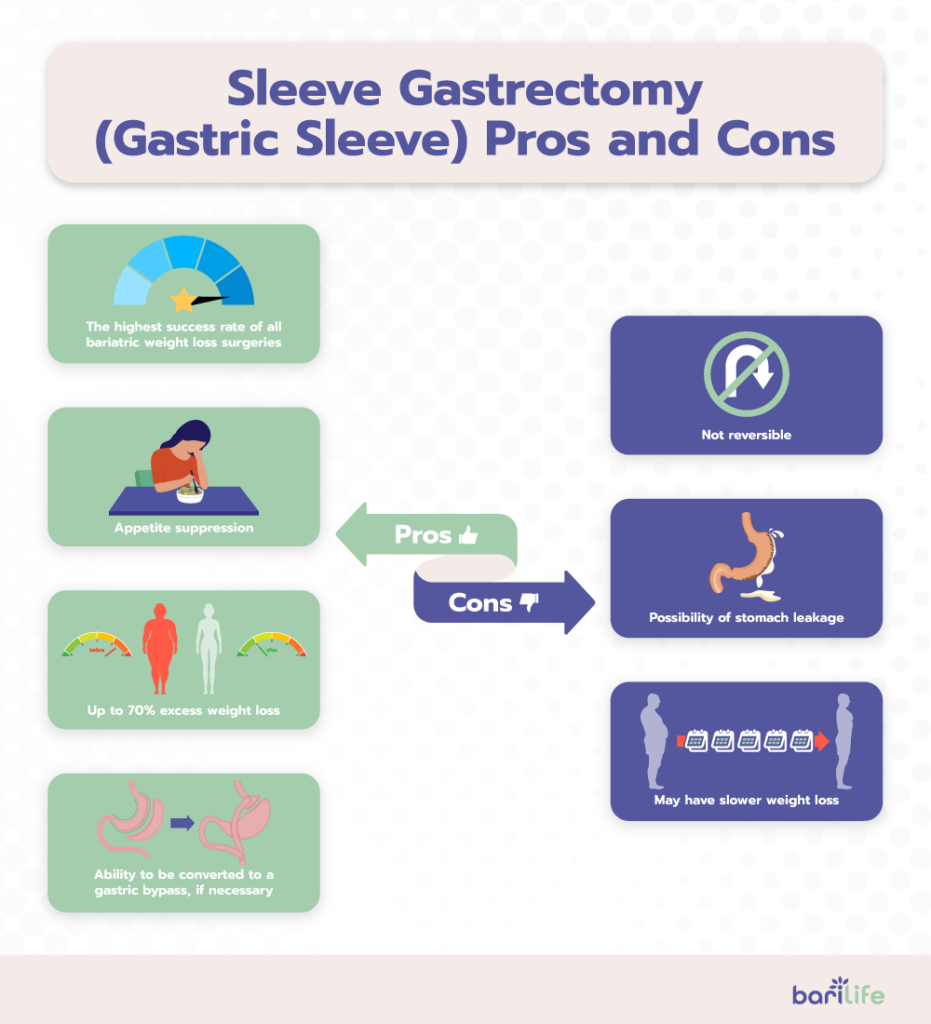
2. Sleeve Gastrectomy (Gastric Sleeve)
A gastric sleeve is one of the more popular bariatric weight loss surgeries, due to its high success rates.
Pros
- The highest success rate of all bariatric weight loss surgeries
- Up to 70% excess weight loss
- Appetite suppression
- Ability to be converted to a gastric bypass, if necessary
Cons
- Not reversible since a portion of the stomach is permanently removed
- Possibility of stomach leakage due to stomach staples
- May have slower weight loss than other procedures
3. Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD with DS)
The BPD with DS is the most invasive of all bariatric weight loss surgeries, but also has the highest %EWL.
Pros
- The highest %EWL – range is between 70-80%
- Reduction of comorbidities
- Decreased risk of dumping syndrome
Cons
- Most invasive procedure
- Higher risk of complications
- Longer post-surgery recovery time
- Increased risk for nutritional deficiencies
4. Gastric Band
A gastric band or lap band is a minimally invasive procedure and also has many pros and cons.
Pros
- Minimally invasive, quick recovery time
- Lower risk than the gastric sleeve, BPD with DS, and gastric bypass
- The band can be removed
- Less likelihood of nutritional deficiencies
Cons
- Slower weight loss than other procedures
- 50% EWL, which is on the lower side when compared to other procedures
- Need for multiple adjustments to increase or decrease stomach restriction
5. Intragastric Balloon
An intragastric balloon is a short-term weight loss alternative, as it has to be removed after 6 months. However, it will help you make healthier lifestyle changes for long-term weight loss.
Pros
- Short-term alternative
- Learning lifestyle changes
- Least invasive surgery type
Cons
- The balloon has to be removed after 6 months
- The lowest percentage of weight loss at 10%
- Least effective in reducing comorbidities
Again, everyone’s bariatric weight loss chart will look different. It depends on your body, procedure type, and excess body weight. Work with your surgeon to determine which bariatric weight loss surgery is right for you.
Factors That Can Affect Weight Loss
When reviewing the bariatric weight loss chart, remember that everyone is different. There are several factors that can affect your weight loss journey. Let’s examine some ways to maximize your weight loss.
- Stick to your diet: Always adhere to the guidelines of which phase of the bariatric post-op diet you are in. This will help you achieve maximum weight loss and prevent unnecessary complications by not sticking to your diet. Phase 4 of the bariatric post-op diet, which is the final or stabilization phase, also has guidelines. Remember, you are not just dieting to lose weight, but are also changing your lifestyle and creating new healthy eating habits.
- Exercise: Exercise is another essential component of weight loss. Weight loss should come easy and naturally after surgery. However, to continue weight loss and avoid a weight loss plateau, you have to exercise. Slowly introduce cardio and strength exercises into your routine to help you build muscle to burn fat.
- Check your mental health: Poor mental health and well-being can increase your risk for weight regain after bariatric surgery. It’s crucial to not only check on your physical health but also your mental health. Try cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) after weight loss surgery. It may help you avoid weight regain and lose weight faster.
Again, everyone is different and will have varying weight loss timelines and percentages of excess weight loss. Weigh the pros and cons of each procedure and discuss your options with your surgeon. They can even help you create your own bariatric weight loss chart!
References
https://www.livestrong.com/article/447243-is-it-a-myth-that-muscle-burns-more-calories-than-fat/
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11695-009-9895-6
https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/assessing/bmi/adult_bmi/english_bmi_calculator/bmi_calculator.html
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3744630/
http://www.assessmentpsychology.com/metlife.htm




What are your tips and tricks to post-bariatric success?