What is bariatric surgery? Bariatric surgery has helped many people lose weight and improve their health. It is important to consider both the bariatric surgery cost and whether bariatric surgery safe practices were followed. But, some may need a second step on their journey. Ramped position bariatric patients may require specific adjustments to ensure safety during surgery
Bariatric revision surgery is for those with complications or poor weight loss after their first procedure. This surgery aims to fix the previous operation. It may provide a new chance for success. But how do you know if bariatric revision surgery is the right choice for you? This article will explore who might benefit from it. It will cover the types of revisions available and what to expect from the process.
Table of Contents
What is Bariatric Revision Surgery?
Bariatric revision surgery is done to correct, modify, or enhance the outcome of a previous weight-loss surgery. It is typically performed after non-reversible procedures like gastric sleeve or gastric bypass, often due to medical complications or insufficient weight loss. Conditions that may necessitate bariatric revision surgery include gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), malnutrition, ulcers, strictures, or other complications arising from the initial surgery.
There are three types of bariatric revisions. Conversion surgeries can change one procedure to a different procedure. For instance, a patient may initially undergo gastric band surgery, which is a reversible bariatric surgery, and later opt for a gastric bypass. This approach is also common for patients needing to lose more weight before qualifying for a more invasive procedure. Corrective surgeries can address anatomical issues that are a result of the initial surgery. Reversal surgeries restore the original anatomy and can be done for severe complications.
Patients undergoing revision surgery must pay particular attention to their nutrient intake, such as ensuring adequate bariatric vitamins, which are crucial for maintaining health after surgery. Many patients prefer bariatric vitamins chewable for easier consumption post-surgery.
Why Might Someone Need Revision Surgery?

It can be difficult for a patient to experience significant weight regain or fail to lose enough weight after the initial surgery. Because of this, they may choose to proceed with a revision surgery. In a study that compared revisional and primary bariatric surgery, 64% of patients were referred for revision due to weight regain.
Revision surgery may be indicated when issues such as pouch dilation, band slippage, or severe acid reflux arise. A revision surgery may alleviate these symptoms that are a result of the initial procedure.
Bariatric surgeries can have a beneficial impact on hormones that support weight loss and can improve insulin sensitivity, however, there is also the possibility of changes in the body’s metabolic or hormonal responses post-surgery limiting the long-term effectiveness of the initial bariatric surgery. Reductions in vitamin D and the hormones leptin and estrogen are especially important to be aware of.
It has been suspected that poor follow-up care could be a main cause of postoperative issues that lead to the desire for revisional bariatric surgery
Types of Bariatric Revision Procedures
Individuals who have had an adjustable gastric band procedure may choose to receive a revision procedure to convert the gastric band to a gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy. This is done for the possibility of providing better long-term results. This is considered the gold standard for revisional surgeries, given that it involves removing the band and proceeding with the gastric bypass or gastric sleeve.
This surgery poses the same risks and recovery time as someone who has never had a bariatric surgery. Patients undergoing these surgeries must often incorporate specialized products like bariatric protein shakes, bariatric multivitamins, and bariatric multivitamin with iron to ensure their diet meets nutritional requirements after the procedure.
Another option for revisional surgery is converting a sleeve gastrectomy to a gastric bypass or a duodenal switch procedure. While a sleeve gastrectomy is irreversible, it can still be modified. In a 10-year study of patients who had revision surgery after a sleeve gastrectomy, 87% of revisions were due to ongoing obesity, and 5.2% were due to GERD.
For patients dealing with digestive health issues after surgery, introducing a bariatric probiotic may aid in improving gut health and digestion, especially after complex procedures.

Endoscopic revision techniques offer less invasive options for revision surgery. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) is a non-surgical procedure that can be used as a primary weight-loss treatment or as a revisional procedure after less invasive surgeries like gastric banding or sleeve gastrectomy. A transoral outlet reduction (TORe) also involves adjusting the anatomy endoscopically without major surgery. This is intended for individuals who have lost inadequate weight following gastric bypass surgery.
Evaluation Process for Candidates
A comprehensive medical evaluation is necessary to determine if a patient qualifies for revision surgery. The surgeon should review the patient’s surgical history, weight changes, and any complications they are experiencing. A physical exam, along with diagnostic tests, should be conducted to identify any anatomical issues. Tests such as endoscopies, imaging, and metabolic panels can help pinpoint the cause of medical complications or weight regain.
As part of their post-revision dietary regimen, patients may also need to supplement their protein intake using bariatric protein bars or liquid bariatric vitamin options, which are easier to digest and absorb post-surgery.
A psychological evaluation may be required to ensure that the patient is mentally prepared for the second surgery and understands the necessary lifestyle adjustments. Patients’ attitudes and expectations can be an indicator of the postoperative course.
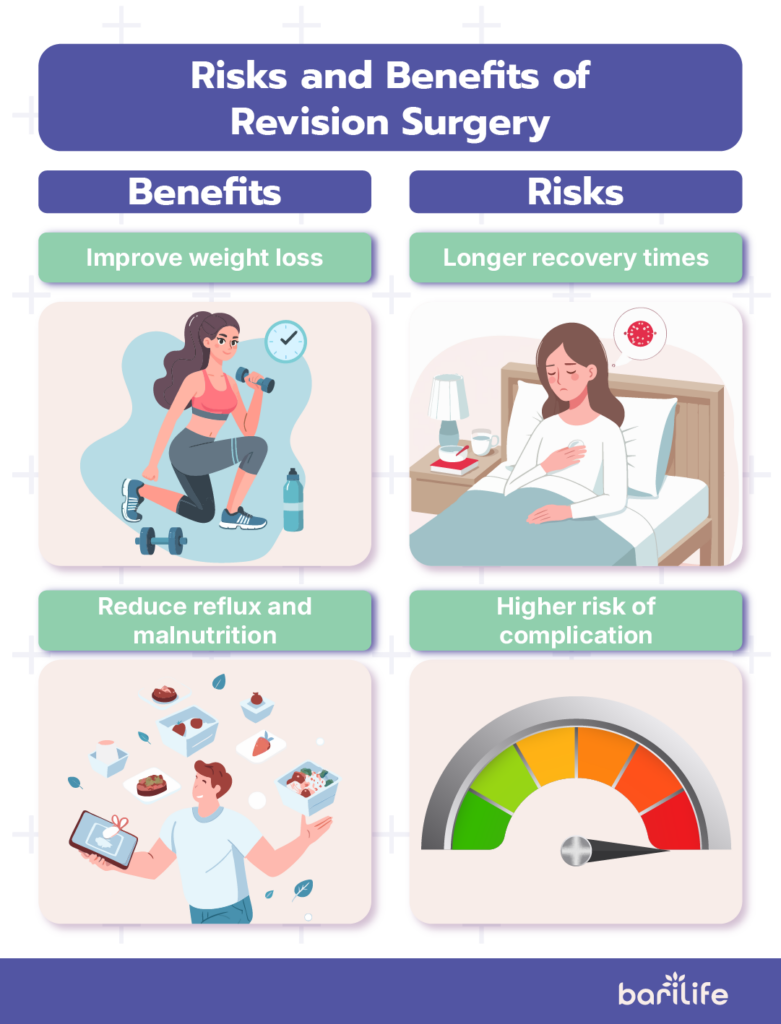
Risks and Benefits of Revision Surgery
As with initial bariatric procedures, revision surgery comes with its own risks and benefits.Revision surgery may have a higher risk of complications and a longer recovery time. This is due to the added complexity and scar tissue from the original surgery. Choosing a revision surgery can improve weight loss. It can also reduce reflux and malnutrition. This will enhance your quality of life.
Revision surgery can involve robotic vs laparoscopic bariatric surgery techniques depending on the patient’s needs. Both approaches have their pros and cons depending on recovery time, precision, and the complexity of the revision.
Bariatric revision surgery can help patients who failed their first surgery. It can also help those with complications from it. It offers them a second chance. But, it’s not a decision to take lightly. You must weigh the risks and benefits, and undergo a thorough evaluation.
You should also understand the specific type of revision surgery that aligns with your health goals. These steps are crucial to see if this option is right for you. With the right support, bariatric revision surgery can help you. It may improve your long-term health and help you lose weight.
Conclusion
Bariatric revision surgery provides a critical option for individuals who have experienced complications or insufficient weight loss following their initial bariatric procedure. It addresses issues such as weight regain, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and other complications. Options for revision include conversion, corrective, or reversal surgeries, depending on the patient’s needs. A thorough evaluation, including medical, physical, and psychological assessments, is essential to determine candidacy. While risks are higher due to previous surgeries, bariatric revision can offer improved health outcomes and weight loss success. With proper support, including attention to nutrition through supplements like Bari Life bariatric vitamins, patients can achieve enhanced long-term health and weight management.




What are your tips and tricks to post-bariatric success?